AZ-900 Certificate Preparation
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Certification Course (AZ-900) - Pass the exam in 3 hours! - YouTube
- AZ-900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Free Full Course and Study Guide | Marczak.IO | Adam Marczak
- Adam Marczak - Azure for Everyone - YouTube
- exampro.co
- Azure Fundamentals AZ 900 Practice Exam Microsoft Certification ~ Azure Crunch
- AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals Study Cram - 2022 Edition! - OVER 500,000 VIEWS! - YouTube
- AZ-900 | Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Full Course, Free Practice Tests, Website and Study Guides - YouTube
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Certification Course (AZ-900) - Pass the exam in 3 hours
-
0066-0167-8531
-
Cloud Services
- compute
- storage
- networking
- databases
Benefits of cloud computing
- cost-effective PAYG
- global
- secure
- reliable - data backup, disaster recovery and data replication, fault tolerance
- scalable - increase or decrease resources and services based on demand
- elastic - automate scaling during spikes and drop in demand
- current - hardware and software is patched, upgraded and replaced by cloud provider
Types of cloud computing
- SaaS - Gmail, Ofice365
- PaaS
- you: deployment and management of your apps
- provider: provisioning, configuring, understanding the hardware or OS
- examples: Elastic beanstalk, Heroku, Google app engine
- IaaS
- you networking features, computers and data storages
- provider: IT staff, data centers, hardware
- examples: Azure, AWS, Oracle cloud
Types of cloud computing responsibilities
- on-premise
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
Cloud deployemnent models
- public cloud
- private cloud (company data centers)
- hybrid - uses both, connected via express route
- cross-cloud - multiple cloud providers (Azure arc)
Total cost of ownership
- CAPEX: monye spent on physical infrastructure
- OPEX : non-physical costs
- leasing software
- training
- paying for cloud support
Cloud architechture terminology
- availability - ability to ensure a service remains available
- scalability - ability to grow rapidly or unimpeded
- elasticity ability to prevent a failure
- fault tolerance - ability to prevent a failyre
- disaster recovery - ability to recover from a failure
Azure VPN Gateway service
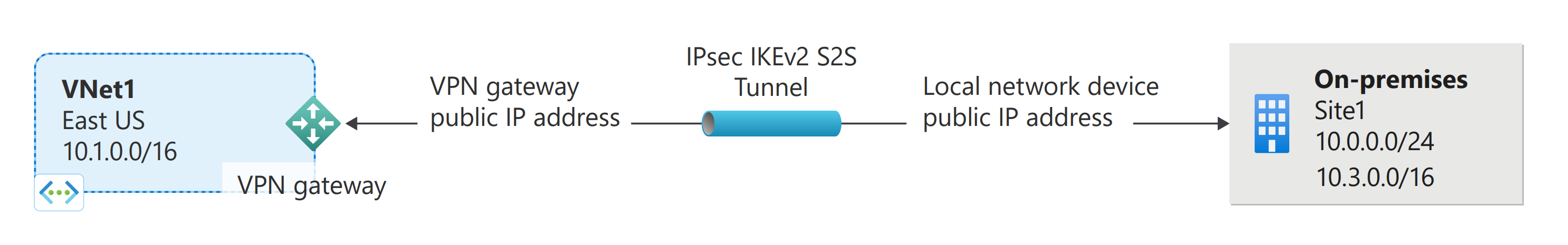
Azure VPN Gateway is a service that uses a specific type of virtual network gateway to send encrypted traffic between an Azure virtual network and on-premises locations over the public Internet. You can also use VPN Gateway to send encrypted traffic between Azure virtual networks over the Microsoft network. Multiple connections can be created to the same VPN gateway. When you create multiple connections, all VPN tunnels share the available gateway bandwidth.
What is Microsoft Sentinel?
Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native solution that provides:
Security information and event management (SIEM)
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR)
Microsoft Sentinel delivers intelligent security analytics and threat intelligence across the enterprise. With Microsoft Sentinel, you get a single solution for attack detection, threat visibility, proactive hunting, and threat response.
Microsoft Sentinel is your bird's-eye view across the enterprise alleviating the stress of increasingly sophisticated attacks, increasing volumes of alerts, and long resolution time frames
How network security groups filter network traffic
You can use an Azure network security group to filter network traffic to and from Azure resources in an Azure virtual network. A network security group contains security rules that allow or deny inbound network traffic to, or outbound network traffic from, several types of Azure resources. For each rule, you can specify source and destination, port, and protocol.
You can deploy resources from several Azure services into an Azure virtual network. For a complete list, see Services that can be deployed into a virtual network. You can associate zero, or one, network security group to each virtual network subnet and network interface in a virtual machine. The same network security group can be associated to as many subnets and network interfaces as you choose.
Resource locks
As an administrator, you can lock an Azure subscription, resource group, or resource to protect them from accidental user deletions and modifications. The lock overrides any user permissions.
You can set locks that prevent either deletions or modifications. In the portal, these locks are called Delete and Read-only. In the command line, these locks are called CanNotDelete and ReadOnly.
CanNotDelete means authorized users can read and modify a resource, but they can't delete it.
ReadOnly means authorized users can read a resource, but they can't delete or update it. Applying this lock is similar to restricting all authorized users to the permissions that the Reader role provides.
Unlike role-based access control (RBAC), you use management locks to apply a restriction across all users and roles. To learn about setting permissions for users and roles, see Azure RBAC.
What is an availability set?
An availability set is a logical grouping of VMs that allows Azure to understand how your application is built to provide for redundancy and availability. We recommended that two or more VMs are created within an availability set to provide for a highly available application and to meet the 99.95% Azure SLA. There is no cost for the Availability Set itself, you only pay for each VM instance that you create.
How do availability sets work?
- http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/support/legal/sla/virtual-machines
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/availability-set-overview
“Availability Set” refers to two or more Virtual Machines deployed across different Fault Domains to avoid a single point of failure.
Each virtual machine in your availability set is assigned an update domain and a fault domain by the underlying Azure platform. Each availability set can be configured with up to three fault domains and twenty update domains. These configurations can't be changed once the availability set has been created.
Update domains indicate groups of virtual machines and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time.
When more than five virtual machines are configured within a single availability set with five update domains, the sixth virtual machine is placed into the same update domain as the first virtual machine, the seventh in the same update domain as the second virtual machine, and so on. The order of update domains being rebooted may not proceed sequentially during planned maintenance, but only one update domain is rebooted at a time. A rebooted update domain is given 30 minutes to recover before maintenance is initiated on a different update domain.
Fault domains define the group of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch.
By default, the virtual machines configured within your availability set are separated across up to three fault domains. While placing your virtual machines into an availability set doesn't protect your application from operating system or application-specific failures, it does limit the impact of potential physical hardware failures, network outages, or power interruptions.
What is Azure Government?
US government agencies or their partners interested in cloud services that meet government security and compliance requirements, can be confident that Microsoft Azure Government provides world-class security and compliance. Azure Government delivers a dedicated cloud enabling government agencies and their partners to transform mission-critical workloads to the cloud. Azure Government services can accommodate data that is subject to various US government regulations and requirements.
Azure Power Shell
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
Local and Virtual Network Gateways
Local and virtual network gateways are virtual private network (VPN) gateways that are used to connect to on-premises networks and encrypt all traffic going between Azure Virtual Network (VNet) and a local network. Each virtual network can have only one virtual network gateway, but one virtual network gateway can be used to configure multiple VPN connections.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets
let you create and manage a group of load balanced VMs. The number of VM instances can automatically increase or decrease in response to demand or a defined schedule. Scale sets provide the following key benefits:
Easy to create and manage multiple VMs
Provides high availability and application resiliency by distributing VMs across availability zones or fault domains
Allows your application to automatically scale as resource demand changes
Works at large-scale
Azure App Service
Azure App Service is an HTTP-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile back ends. You can develop in your favorite language, be it .NET, .NET Core, Java, Ruby, Node.js, PHP, or Python. Applications run and scale with ease on both Windows and Linux-based environments.
App Service not only adds the power of Microsoft Azure to your application, such as security, load balancing, autoscaling, and automated management. You can also take advantage of its DevOps capabilities, such as continuous deployment from Azure DevOps, GitHub, Docker Hub, and other sources, package management, staging environments, custom domain, and TLS/SSL certificates.
What is Advisor?
Advisor is a personalized cloud consultant that helps you follow best practices to optimize your Azure deployments. It analyzes your resource configuration and usage telemetry and then recommends solutions that can help you improve the cost effectiveness, performance, Reliability (formerly called High availability), and security of your Azure resources.
With Advisor, you can:
- Get proactive, actionable, and personalized best practices recommendations.
- Improve the performance, security, and reliability of your resources, as you identify opportunities to reduce your overall Azure spend.
- Get recommendations with proposed actions inline.
Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure
Microsoft Cloud Adoption framework (CAF) is a proven guidance that is designed to help organizations to excel in their cloud journey. This framework guides us through various phases of journey starting from why cloud, what to move, where to move, how to move, how to manage & operate in cloud.
This framework provides a set of tools, templates, guidance, and narratives at every stage to accelerate your cloud adoption journey and it starts with
- Strategy: which is to understand the strategy and motivations to adopt cloud.
- Plan : Evaluating the readiness and adoption plan for planning your cloud estate.
- Ready: Setting up the Azure landing zone and implement the best practices for future expansion.
- Adopt: Discovering the migration/cloud native/hybrid scenarios for your workloads to act on your scenarios.
- Govern: Assess the current and end-state with a vision and iteratively add those controls to avoid any tangible risk in future.
- Manage: Document all operations/management baseline, design principles for landing new workloads and supporting existing workloads.

Cloud architecture terminologies
- reliability, availability - data backup, disaster recovery and data replication, fault tolerance. [HA] Highly availablr
- scalable - increase or decrease resources and services based on demand
- elastic - automate scaling during spikes and drop in demand
- current - hardware and software is patched, upgraded and replaced by cloud provider
- fault tolerance - ability to prevent a failure
- disaster recovery - ability to recover from a failure. [DR] Highly Durable
High availability
Ability to remain available for your services by ensuering there is no single point of failure and/or ensure a certain level of performance
Running your workload across multiple AZ ensures that if 1 or 2 AZs become unavailable your service / applications remains available.

High Scalability
- vertical scaling - upgrade to bigger server
- horizontal scaling - add more servers
High Elasticity
Ability to automatically increase or decrease your capacity based on current demand of traffic, momory and computing power
Azure BM scale sets - automatically iincrease or decrease in response to demand or a defined structure
Fault tolerance - High Durability
Ability tp recover from disaster.
DR - Disaster recovery
Evolution of computing
Dedicated > VMs > Containers > Functions
Regions and Geographies
A region is a grouping of multiple data centers
Azure operates in multiple datacenters around the world. These datacenters are grouped in to geographic regions, giving you flexibility in choosing where to build your applications.
You create Azure resources in defined geographic regions like 'West US', 'North Europe', or 'Southeast Asia'. You can review the list of regions and their locations. Within each region, multiple datacenters exist to provide for redundancy and availability. This approach gives you flexibility as you design applications to create VMs closest to your users and to meet any legal, compliance, or tax purposes.
- 58 regions
- 140 countries
Paired regions
Each Azure region is paired with another region within the same geography (such as US, Europe, or Asia). This approach allows for the replication of resources, such as VM storage, across a geography that should reduce the likelihood of natural disasters, civil unrest, power outages, or physical network outages affecting both regions at once. Additional advantages of region pairs include:
- In the event of a wider Azure outage, one region is prioritized out of every pair to help reduce the time to restore for applications.
- Planned Azure updates are rolled out to paired regions one at a time to minimize downtime and risk of application outage.
- Data continues to reside within the same geography as its pair (except for Brazil South) for tax and law enforcement jurisdiction purposes.
An Azure geography is an area of the world that contains at least one Azure region. For example, India is a geography. Similarly United States and United Kingdom are geographies.
Azure Government (US)
Azure Managed Disks
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
- Replicates your data three times within the region in which you created your storage account.
Storage account-based disks
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
- Replicates your data three times within the region in which you created your storage account.
- Zone redundant storage (ZRS)
- Replicates your data three times across two to three facilities, either within a single region or across two regions.
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Replicates your data to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region.
- Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
- Replicates your data to a secondary region, as with GRS, but also then provides read-only access to the data in the secondary location.
The following table provides a quick overview of the differences between the storage replication types:
| Replication strategy | LRS | ZRS | GRS | RA-GRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data is replicated across multiple facilities. | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data can be read from the secondary location and from the primary location. | No | No | No | Yes |
| Number of copies of data maintained on separate nodes. | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
Region types and service availability
- recommended regions
- Alternate (other) region
- GA General availability - ready to be used publicly by everyone
- Availability
- foundational - recommended + other
- mainstream - recommended; other - based on customer demand
- specialized - recommended, other - nased on customer demand
Special regions
Compliance and legal reasons
-
first
-
second
-
third
-
US Dod Central
-
US Gov Virginia
-
US Gov lowa
China
MS does not directly maintain
- China East
- China North
Availablity Zones
Region - 3 availability zones
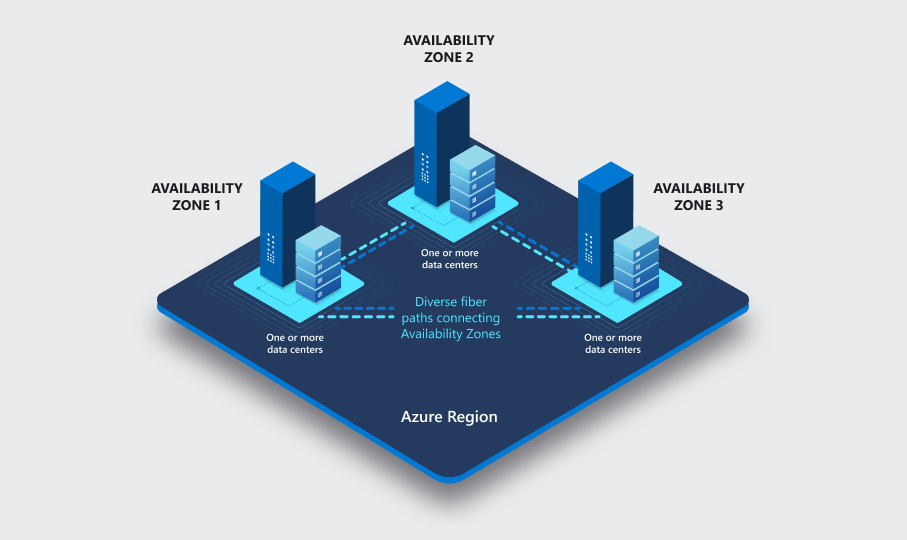
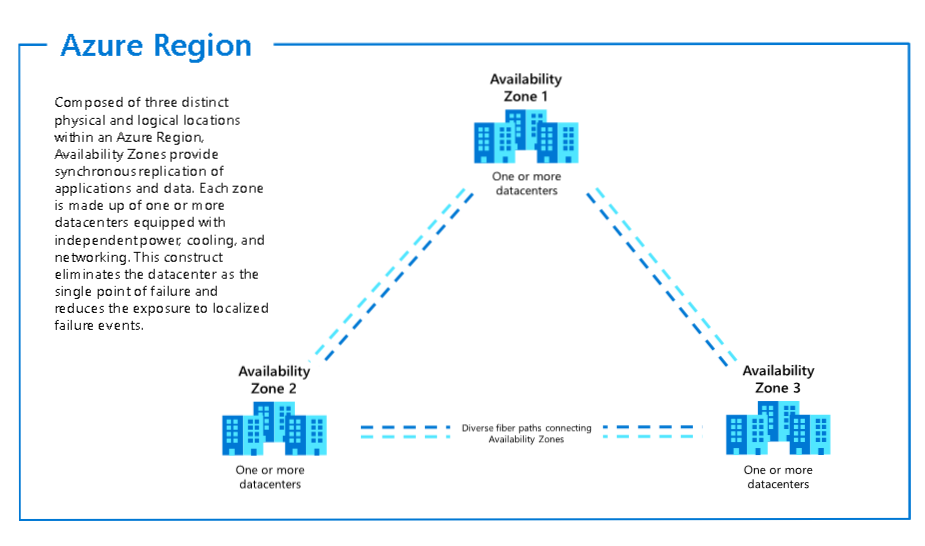
AZ supported regions
Alternate or Others regions do not support availability zones.
Recommended regions are suppose to have at least 3 AZs.
Fault and update domains
Fault domains
define the group of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch.
By default, the virtual machines configured within your availability set are separated across up to three fault domains.
While placing your virtual machines into an availability set doesn't protect your application from operating system or application-specific failures, it does limit the impact of potential physical hardware failures, network outages, or power interruptions.
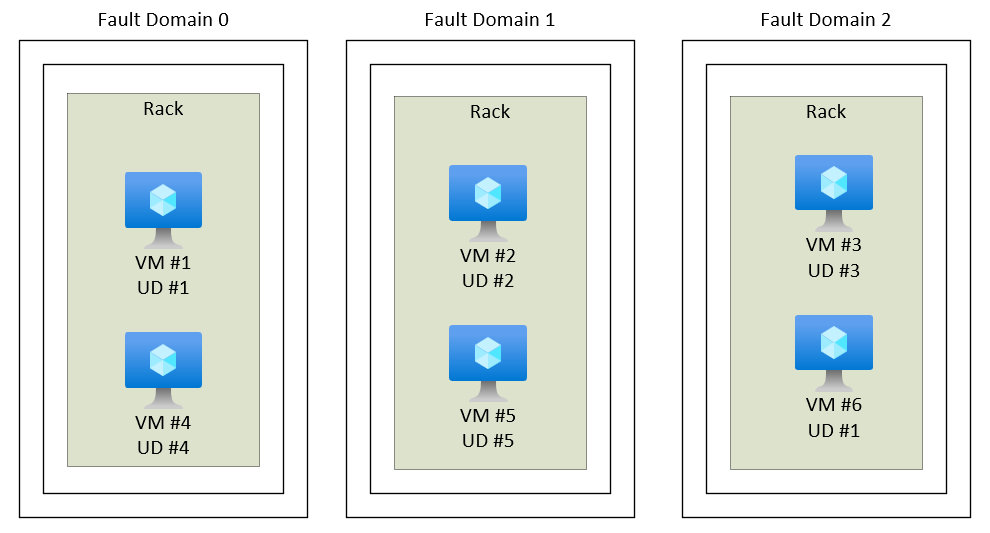
Update Domain
ensures that Azure performs it's software updates from time to time. The resources are isolated.
Update domains indicate groups of virtual machines and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time. When more than five virtual machines are configured within a single availability set with five update domains, the sixth virtual machine is placed into the same update domain as the first virtual machine, the seventh in the same update domain as the second virtual machine, and so on. The order of update domains being rebooted may not proceed sequentially during planned maintenance, but only one update domain is rebooted at a time. A rebooted update domain is given 30 minutes to recover before maintenance is initiated on a different update domain.
An availability set
is a logical grouping of VMs that allows Azure to understand how your application is built to provide for redundancy and availability. We recommended that two or more VMs are created within an availability set to provide for a highly available application and to meet the 99.95% Azure SLA. There is no cost for the Availability Set itself, you only pay for each VM instance that you create.
Computing services
Azure virtual machines
Azure container instances - Docker as a service
Azure kubernetes
Azure service fabric - Tier-1 enterprise containers as a service. Distributed systems platform
Azure functions - event-driven, serverless compute. You pay only for the compute time you consume.
Azure batch - batch computer workloads. Use Spot VMs to save money (low-priority VMs)
Storage services
Azure blob storage
Object Serverless Storage
Store very large files and large amounts of unstructured date.
Azure Disk Storage
Virtual volume. Attached to VM.
Azure file storage
Shared volume
Azure queue storage
A data store for queuing and reliably delivering messages between applications
Azure Table Storage
Wide-Column NoSQL Data base
Azure Data box
A rugged briefcase computer and storage designed to move terabytes or petabytes of- Text field
Azure Archive Storage
Long term cold storage
Azure Data Lake storage
A centralized repository that allows you to store all your structured and unstructured data at any scale
Database services
Azure Cosmos DB
NoSQL database
Azure SQL Database
MS SQL database
Azure Database for MySQL
MySQL/PostgreSQL/MariaDB
SQL Server on VMs
Azure Synapsis Analytics
Azure Database Migration Service
Azure Cache for Redis
Aches frequently used and static data to reduce data and application latency
Azure Table Storage
Application Integration Services
Azure Notifications Hub
Pub/Sub Send push notifications to any platform from any back end
Azure API Apps
API gateway Quickly build and consume APIs in hte cloud. Route APIs to Azure Services
Azure Service Bus
Reliable cloud messaging as a service MaaS and simple hybrid integration
Azure Stream Analytics
Serverless real-time analytics, from the cloud to the edge
Azure Logic Apps
Schedule, automate and orchestrate tasks, businesses processes and workflows.
Azure API Management
Put in-front of existing APIs to add additional functionality
Azure Queue Storage
A data store for queuing and reliably delivering messages between applications
Developer and Mobile tools
Azure SignalR Service
Real-Time Messaging Easily add real-time web functionality to applications
Think of it like the Pusher for Azure
Azure App Service
Easy to use service for deploying and scaling web-applications with .Net, Node.js Java, Python and PH
Developer focus on building their web-apps, and not worry about the underlying infrastructure
Think of it like Heroku for Azure
Visual Studio (Microsoft-owned)
Code Editor The integrated development environment (IDE) designed for creating powerful, scalable
applications for Azure
Xamarin (Microsoft-owned)
Mobile-App Framework Create powerful and scalable native mobile apps with .NET and Azure
Azure DevOps Services
Azure DevOps
Plan smarter, collaborate , and ship faster with a set of modern dev services.
Azure Boards
Kanban Deliver value to your users faster using proven agile tools to plan, track, and discuss work
across your teams.
Azure Pipelines
Build, test, and deploy with CI/CD that works with any language, platform, and cloud. Connect to
GitHub or any other Git provider and deploy continuously.
Azure Repos
Get unlimited, cloud-hosted private Git repos and collaborate to build better code with pull requests
and advanced file management.
Azure Test Plans
Test and ship with confidence using manual and exploratory testing tools.
Azure Artifacts
Create, host, and share packages with your team, and add artifacts to CI/CD pipelines with a single cli
Azure DevTest Labs
Fast, easy, and lean dev-test environments
Azure Resource Manager
What is Infrastructure as code (IaC)?
The process of managing and provisioning computer data centers through machine-readable
definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools.
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) allows you to programmatically create Azure
resources via JSON template.
Azure Quick Start Templates
Azure QuickStart is a library of a pre-made ARM templates provided by the community
and partners to help you quickly launch new projects for a variety of stack scenarios
Azure Virtual Network and Subnets
Virtual Network (vNet) is a logically isolated section of the Azure Network where you
launch your Azure resources. You choose a range of IPS using CIDR Range
CIDR Range of 10.0.0.0/16 = 65,536 IP Addresses
Subnets a logical partition of an IP network
into multiple smaller network segments. You
are breaking up your IP range for VNet into
smaller networks.
Subnets need to have a smaller CIDR range than to the
vNet represent their portion.
eg Subnet CIDR Range 10.0.O.O/24 = 256 IP Addresses
A Public Subnet is one that can reach the internet
A Private Subnet is one that cannot reach the internet
Cloud-Native Networking Services
Azure DNS
Provides ultra-fast DNS responses and ultra-high domain availability
Azure Virtual Network (vNET)
A logical isolated section of the Azure network for customers to launch Azure resources within.
Azure Load Balancer
OSI Level 4 (Transport) Load Balancer
Azure Application Gateway
OSI Level 7 (HTTP) Load Balancer, can apply a Web Application Firewall
Network Security Groups
A virtual firewall at the subnet level
Enterprise / Hybrid Networking Services
Azure Front Door
Scalable and secure entry point for fast delivery of your global applications
Azure Express Route
A connection between your on-premise to Azure cloud from 50 Mbps to 10 Gbps
Virtual WAN
a networking service that brings many networking, security, and routing functionalities
together to provide a single operational interface
Azure Connection
A VPN connection securely connects two Azure local network via (IPsec).
Virtual Network Gateway
A site-to-site VPN connection between an Azure virtual network and your local network
Azure Traffic Manager
Azure Traffic Manager
operates at the DNS layer to quickly and efficiently direct incoming DNS
requests based on the routing method of your choice.
- Route traffic to servers the geographically near by to reduce latency
- Fail-over to redundant systems in-case primary systems become unhealthy.
- Route to random VM to simulate A/B testing
Routing method
- Weighted
- Performance
- Weighted
- Priority
- Geographic
- MultiValue
- Subnet
Azure DNS
Azure DNS
allows you to host your domains names on Azure
You can create DNS Zones and manage your DNS records.
Azure Load Balancer
Azure Load Balancer
is used for evenly distributing incoming network traffic
across a group of backend resources or servers.
Azure Load Balancer operates on OSI Layer 4 (Transport)
You can create a:
- Public Load Balancer incoming traffic from the
internet to public-facing servers (Public IPs) - Internal (Private) Load Balancer incoming internal
network traffic to private-facing servers (Private IPs)
Scale Sets
Allows you group together identical Virtual Machines (VMS) and automatically increase
or decrease the amount of servers based on:
• change in CPU, memory, disk, and network performance
On a predefined schedule
IoT Services
IOT Central
Connects your IOT devices to the cloud
IoT Hub
Enable highly secure and reliable communication between your IOT application and the devices it manage
IoT Edge
A fully managed service built on Azure IOT Hub.. It allows data processing and analysis nearest the IOT devices.
Edge computing is when you offload compute from the cloud to local computing hardware such as IOT devices,
phones or home computers
Windows 10 IOT Core Services
cloud services subscription that provides the essential services needed to commercialize a device on
Windows 10 IOT Core. Long-term OS support and services to manage device updates and assess device health
Bg Data and Analytics
What is BigData?
A term used to describe massive volumes of structured/unstructured data that is so large it is difficult to move and process using traditional database and software techniques.
Azure Synapse Analytics (formally known as SQL Data Warehouse)
Enterprise data warehousing and Big Data analytics.
Intended to run SQL queries against large databases for things such as reporting.
HDInsight
Run open-source analytics software such as Hadoop, Kafka and Spark
Azure Databricks
An Apache Spark-based analytics platform optimized for the Microsoft Azure cloud services platform.
Third-Party Databricks cloud services supported within Azure.
Data Lake Analytics
An on-demand analytics job service that simplifies big data. A data lake is a storage repository that holds a vast amount of raw data in its native format until it is needed
AI/ML Services
What is Artificial Intelligence (Al)?
Machines that perform jobs that mimic human behavior
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machines that get better at a task without explicit programming
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Machines that have an artificial neural network inspired by
the human brain to solve complex problems.
Azure Machine Learning Service
A service for that simplifies running Al/ML related workloads allowing you to build flexible
Pipelines to automate workflow. Use Python an R, Run DL workloads such as Tensorflow
Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic)
An older service that manages Al/ML workloads. Does not have a pipeline and other limitations.
Workloads are not easily transferable to from classic to the new service.