links:: Source Control for Test Automation with Git MOC
4.1 Branches
Create new branch
git branch newbranch
switch branch
git checkout newbranch
git checkout -b newbranch
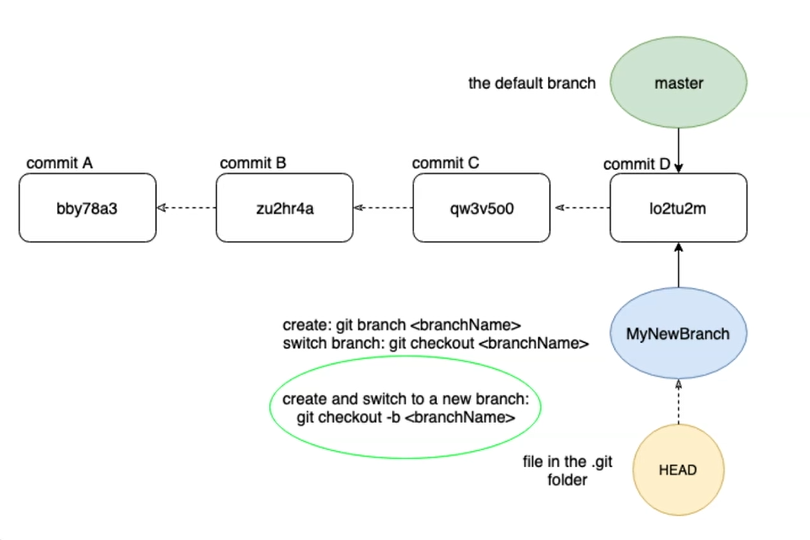
HEAD is a simple file in the .git directory which points to the active branch and thereby to the latest commit of that branch**
Fast-forward Merge
A fast-forward merge means that the master branch pointer HEAD can simply be moved forward to the commit where the “MyNewBranch” is pointing to. All this, because the master branch hasn't diverged through other commits on it from the “MyNewBranch”.
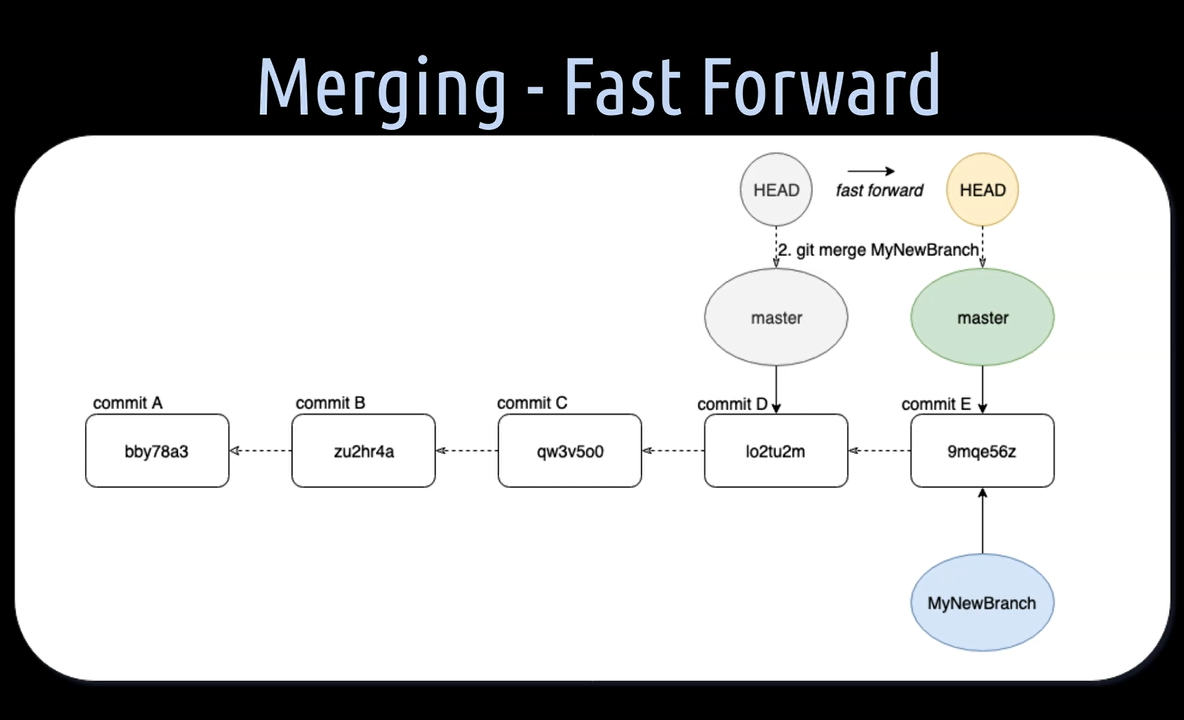
Example: merging 2 branches
- feature/update4-ffmerge-test (make changes)
- feature/update5-ffmerge-test (no changes)
git checkout -b feature/update4-ffmerge-test
Update Files
git commit -am "/update5-ffmerge-test"
git checkout -b feature/update5-ffmerge-test
No Updates
Now Merge Current Branch (feature/update5-ffmerge-test) to feature/update4-ffmerge-test
git merge feature/update4-ffmerge-test
1. Git opens default editor
2. Provide commit message
3. Close editor
4. That's it. Now two branches ar emerged
5. Run `git log` , see additional merge commit
### Merging Diverged Branches
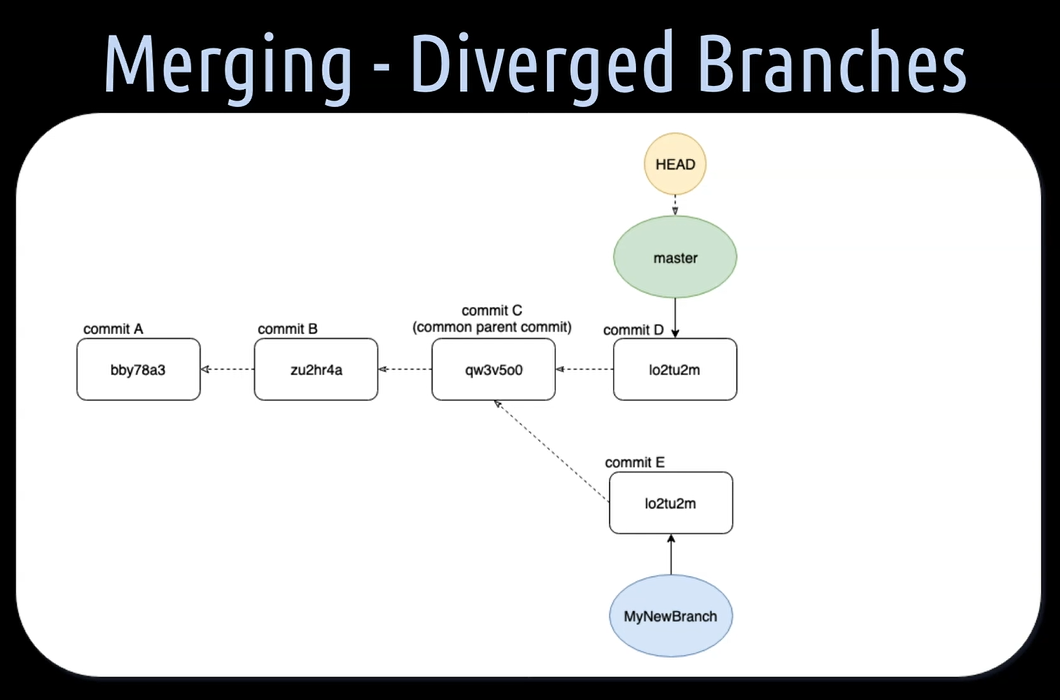
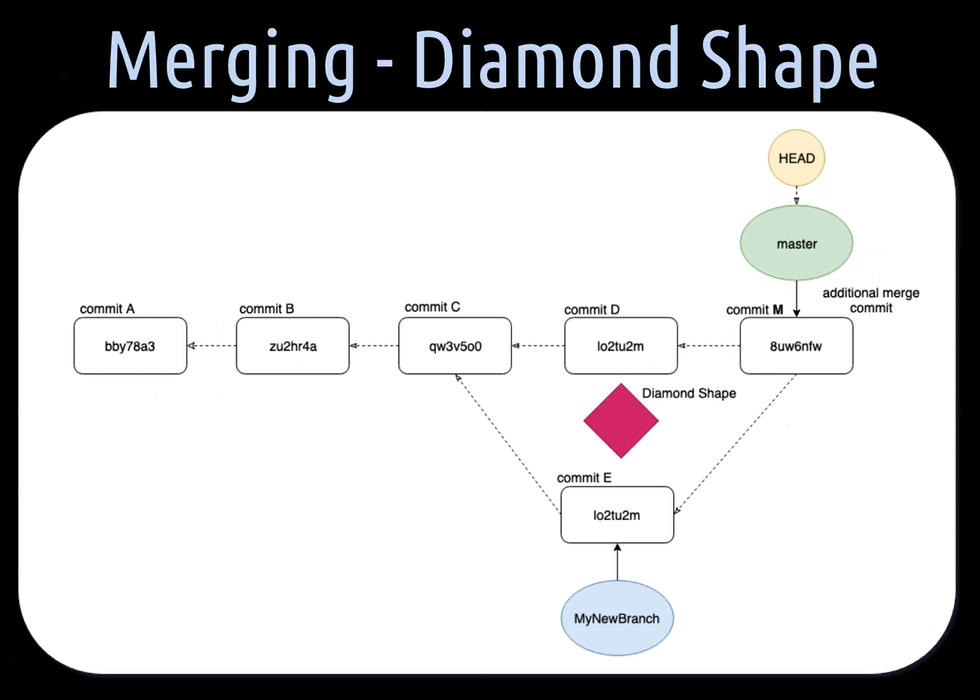
Example: merging 2 branches
- feature/feature/test3-lisa-diverged (make changes)
- feature/new-test-class (make changes)
```bash
git checkout -b feature/feature/test3-lisa-diverged
# update files
git commit -am "update5-ffmerge-test"
git checkout -b feature/new-test-class
# update files
# now merge current branch ( feature/new-test-class) to feature/feature/test3-lisa-diverged
git merge feature/test3-lisa-diverged
Rebasing

When we create a new branch, in our case here, the “MyNewBranch”, we branch away from another branch, in our case here, the master branch. The common parent commit C is the base of commit E of the “MyNewBranch”.
- By applying the concept of rebasing, we can change the base of the commit E.
- By applying the concept of rebasing, we can change this base commit C of the commit E.
Let's checkout the “MyNewBranch” to get with rebasing the latest changes which were made on the master branch, this is commit D, into our “MyNewBranch”.
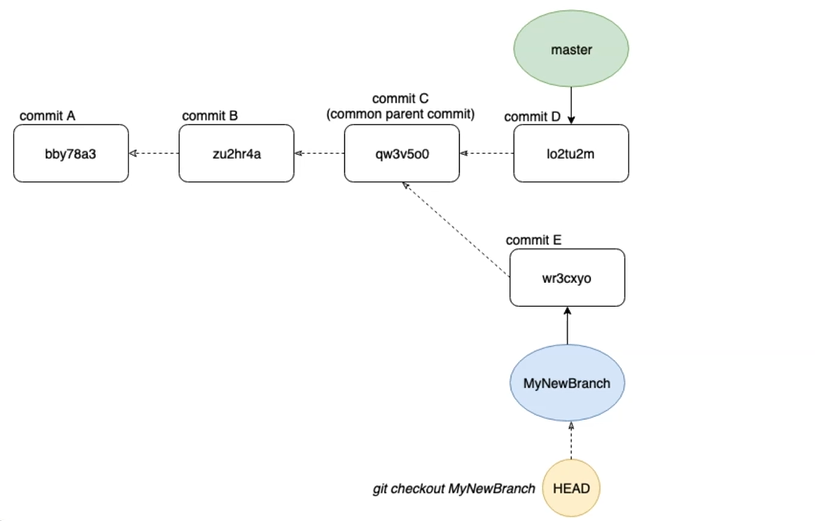
Let's remember when we're checking out a new branch, we just move the HEAD pointer accordingly.
When we now hit git rebase master, we rebase our active “MyNewBranch” onto the current state of the master branch.
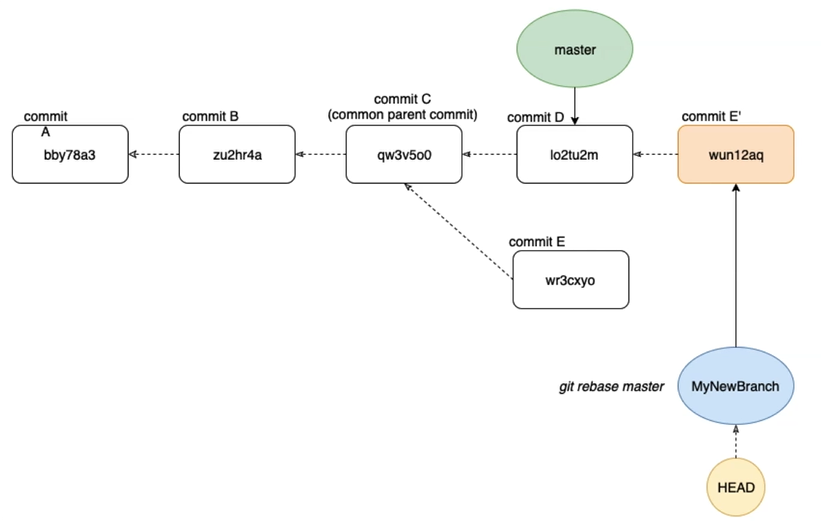
It is important to notice here that we rebase onto the current state of the master branch and not into the master branch itself.
When rebasing, Git will take everything which was in commit E, apply that into a commit E', and then puts E' on the top of the latest commit D, from the master branch.
In other words, we have just rebased the pointer “MyNewBranch” from commit E to a new commit E', which in turn is now referencing the latest commit D, of the master branch.
With using rebase, we can make sure that we frequently integrate the changes which are made on the master branch into our own feature branch. With that, we can keep a clean, linear, shiny history that allows us finally doing a fast-forward merge when it's time to get our feature or bug fix branch into the common master branch.
Keeping a clean, linear commit history makes reading it much more pleasant, useful, and finally traceable, than having a history which is cluttered with merge commits.
Example: merging 2 branches
- feature/feature/test3-lisa-rebase (make changes)
- feature/test4-lisa-rebase (make changes)
git checkout -b feature/feature/test3-lisa-rebase
# update files
git commit -am "add feature/test3-lisa-rebase"
git checkout master
git checkout -b feature/test4-lisa-rebase
# update files
# now merge current branch ( feature/new-test-class) to feature/feature/test3-lisa-diverged
git merge feature/test3-lisa-diverged
git add.
git commit -m "add feature/test4-lisa-rebase"
git checkout feature/test4-lisa-rebase
git rebase feature/test3-lisa-rebase
git push origin
# we need to set upstream for new branch
git push --set-upstream origin feature/test4-lisa-rebase
# now open Github
# create PR
# merge PR (rebase and merge)
git fetch
git checkout master
Creating Pull-request
git fetch
So, we fetch all the new changes which were made on the remote repository master into our local repository master.
git checkout master
git merge
# resolve conflicts if required